(1) Spatial modeling of natural regenration
Highlights
- The success of natural regeneration in silviculture depends on the complex interactions between interventions of stand structure, the natural seed-dispersal processes, and seedling development.
- The eigenvector spatial filtering (ESF) approach allowed for within-patch scale spatial analysis and modeling for seed dispersal and seedling development.
- The ESF model revealed that gentle slope, moderate soil moisture, and low crown closure were essential in achieving potential seedling establishment and growth.
- Distance dependence occurred in seed dispersal and seedling development; while Density dependence was not detected in seedling development.
- The ESF-based spatially varying coefficient (ESF-SVC) model provided differences in the impacts of environmental factors across the regeneration patches, showing that planting a large number of evenly distributed remnant seed trees in the reserved seed tree patch was effective in improving seed dispersal.
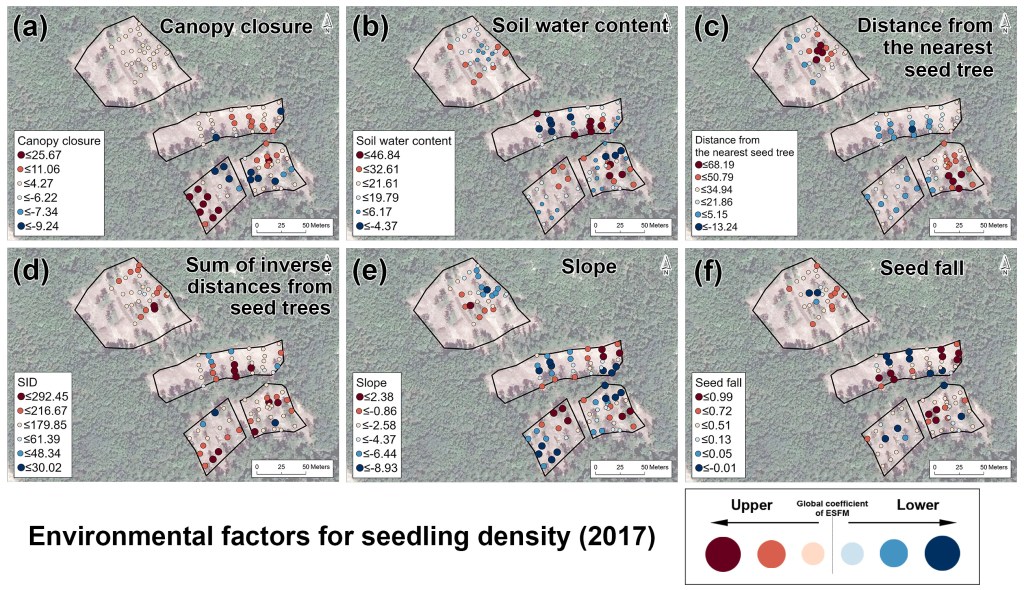
Figure ESF-SVC modeling result for seedling density in 2017, showing local coefficients for each seedling quadrat
(2) Spatial zoning of national park
Highlights
- South Korea has made efforts for the sustainable conservation and use of national parks, but there is a lack of basic data and scientific evaluation system for ecosystem conservation.
- This study aims to develop an ecosystem-based evaluation system to prepare criteria for the 3rd National Park Feasibility Study.
- Essential factors were developed and quantitatively evaluated for each factor, and different weights were applied to each park type for the ecosystem-based evaluation classification criteria.
- The proposed ecosystem-based approach in this study is a scientific and systematic method that considers essential factors for evaluating ecosystem conservation values.

Figure Result of spatial zoning of Jiri Mt. National park
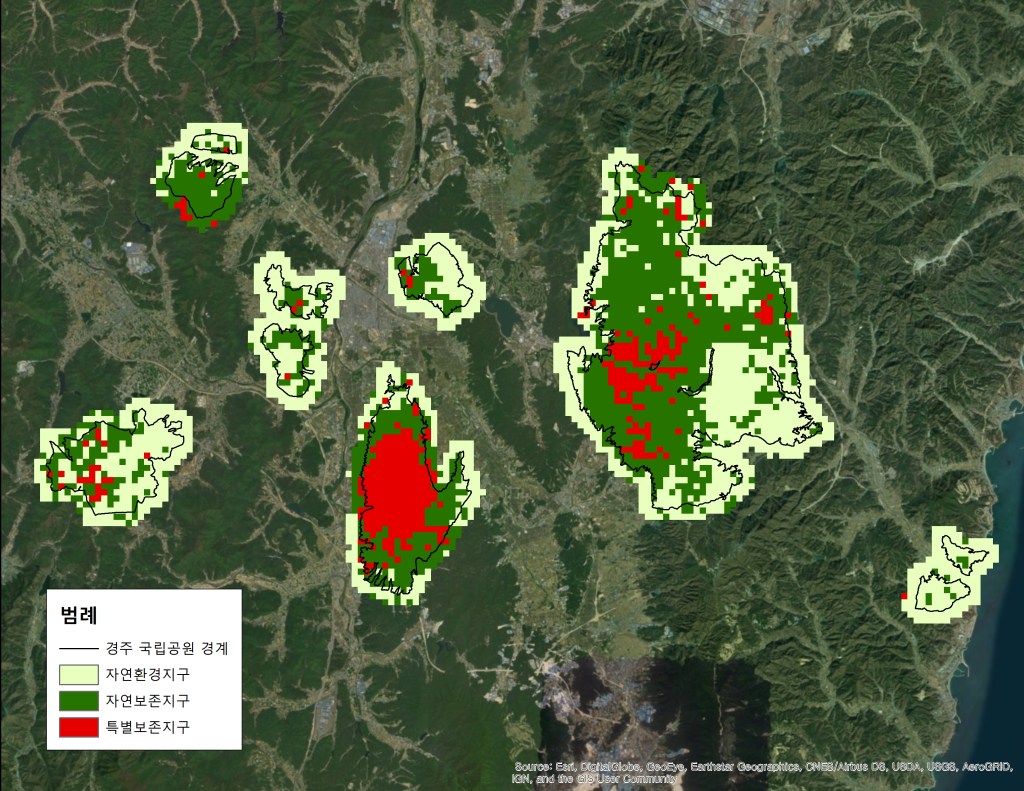
Figure Result of spatial zoning of Kyeongju hitorical National park