(1) COVID-19 transmission dynamics
Highlights
- This study identifies local demographic and socio-economic factors affecting SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the Seoul metropolitan area.
- Geographically weighted lasso (GWL) was used to account for spatial heterogeneity and identify statistically significant regions with specific local characteristics.
- Young adults, Christian population, and subway commuters were the most significant local characteristics that influenced SARS-CoV-2 transmissions in the area.
- Locally targeted intervention policies are required for effective outbreak control.

Figure GWL resul map showing subway commuters significantly impact SARS-CoV-2 tranmission in the Seoul metropolitan area
(2) Risk map of African swine fever and highly pathogenic avian influenza
Highlights
- This section will be updated soon
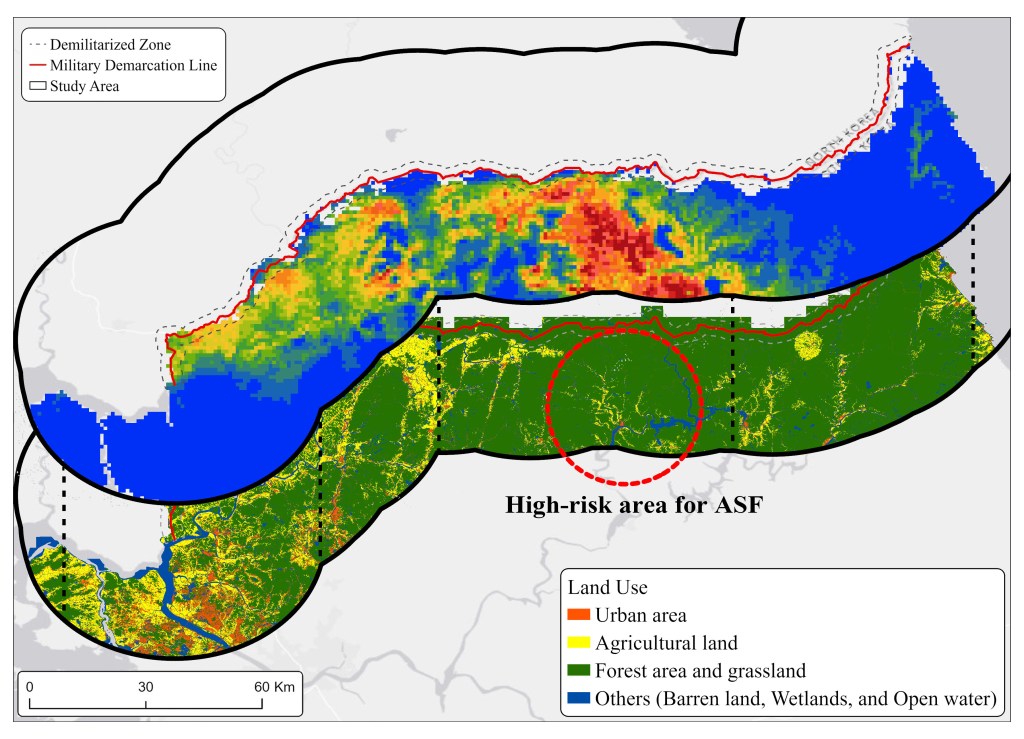
Figure High-risk area for ASF with land use map (it is test map)
(3) Spatial pattern of tuberculosis
Highlights
- S. Korea has the highest TB incidence rate among OECD countries, reflecting the socio-economic and environmental conditions of the society.
- The study investigates the TB incidences in Korea in socio-economic and environmental perspectives, using Eigenvector spatial filtering to account for spatial autocorrelation and Getis-Ord statistic to track changes in TB clusters.
- The results show that demographic factors such as population composition ratio and growth rate, as well as health insurance payment and public health variables, are significant throughout the study period.
- Environmental variables have a minor effect on TB incidence.
- The study suggests that the unique demographic features of Korea pose a potential threat to TB control in the future.

Figure Average of TB incidence rate (2008-2016)

Figure Spatial patterns of TB hotspot and coldspot (2008-2016)
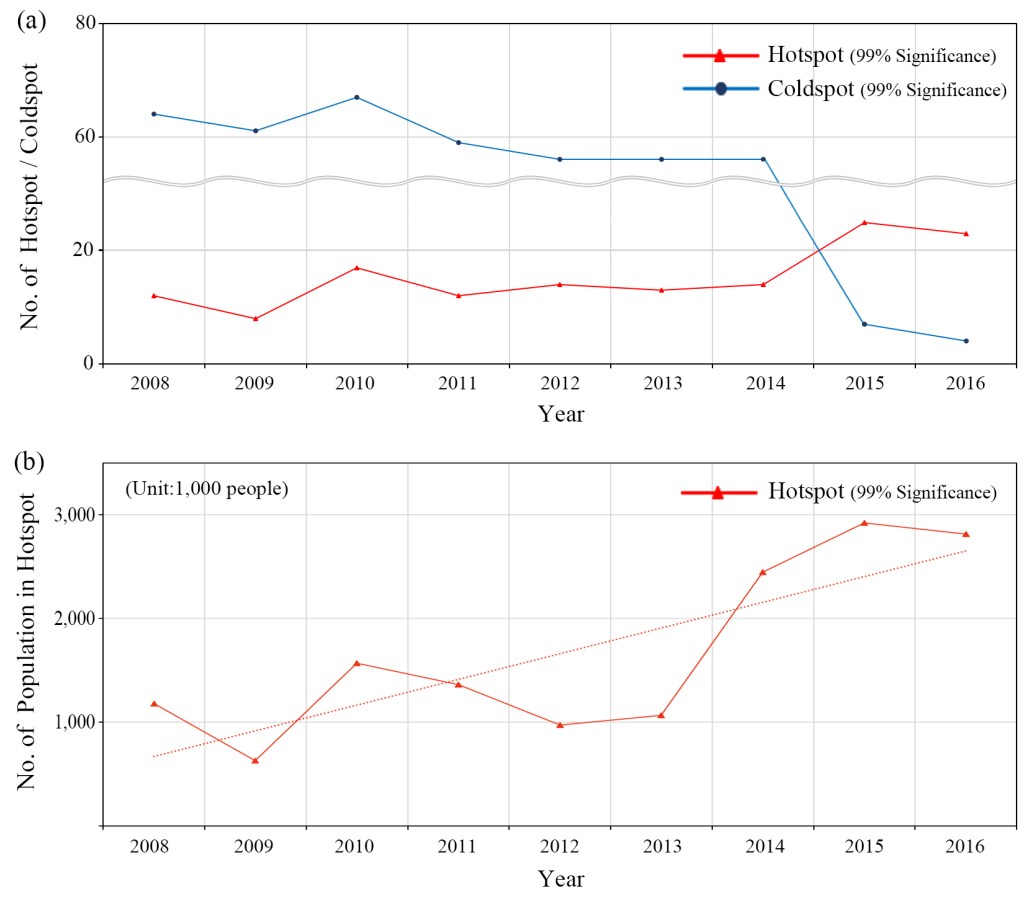
Figure. Changing trend of the number of hotspot and coldspot (upper); the number of populations in hotspot (lower)